Spontaneous adverse event reporting
Session: Poster Session A
(347) Post-marketing safety of ALK inhibitors: an analysis of EudraVigilance reports between 2012 and 2022
Monday, August 26, 2024
8:00 AM - 6:00 PM CEST
Location: Convention Hall II
- NÄ
NanÄa Äebron Lipovec, PhD
Teaching assistant
University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Pharmacy
Ljubljana, Slovenia - LK
Lea Knez
University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Pharmacy
Ljubljana, Slovenia
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
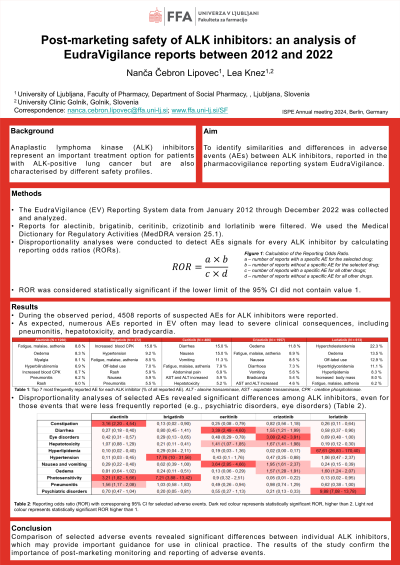
Background: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors represent an important treatment option for patients with ALK-positive lung cancer but are also characterised by different safety profiles.
Objectives: To identify similarities and differences in adverse events (AEs) between ALK inhibitors, reported in the pharmacovigilance reporting system EudraVigilance.
Methods: This study summarized the types and frequencies of AEs of ALK inhibitors. The EudraVigilance Reporting System data from January 2012 through December 2022 was collected and analyzed. Reports for crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib,and lorlatinib were filtered. We used the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA version 25.1). Disproportionality analyses were conducted to detect AEs signals for every ALK inhibitor by calculating reporting odds ratios (RORs). Reports were considered statistically significant if the lower limit of the 95% CI did not contain value 1.
Results: During the 2012-2022 observation period, 4508 reports of suspected adverse reactions to all ALK inhibitors were reported to EudraVigilance, with crizotinib being the most frequently reported (43.4%), followed by alectinib (28.0%), lorlatinib (13.6%), ceritinib (9.0%) and lastly brigatinib (6.0%). The most common adverse event reported in EudraVigilance for each drug include oedema for crizotinib, diarrhoea and nausea for certinib, fatigue for alectinib, elevated blood creatine phosphokinase levels for brigatinib and hypercholesterolaemia for lorlatinib. Disproportionality analyses of selected adverse events revealed significant differences between ALK inhibitors. Oedema was significantly related to crizotinib (ROR 1.57) and lorlatinib (ROR 1.60), hepatotoxicity to crizotinib (ROR 1.86), nausea and vomiting as well as diarrhea to crizotinib (ROR 1.95 and 1.55) and ceritinb (ROR 3.64 and 3.39), constipation to alectinib (ROR 3.16), eye disorders to crizotinib (3.02), photosensitivity to brigatinib (ROR 8.77) and alectinib (2.49), hypertension to brigatinib (17.76) and pnemunotis to alectinib (ROR 1.53) Lorlatinib was also signifcantly related to hyperlipidemia and psychiatric disorders (exact ROR to be evaluated).
Conclusions: This study highlights significant variability in the safety profiles of ALK inhibitors, with each drug associated with distinct adverse events as reported in the EudraVigilance system over a decade. It also indicates the importance of tailored patient management strategies based on the specific ALK inhibitor used.
Objectives: To identify similarities and differences in adverse events (AEs) between ALK inhibitors, reported in the pharmacovigilance reporting system EudraVigilance.
Methods: This study summarized the types and frequencies of AEs of ALK inhibitors. The EudraVigilance Reporting System data from January 2012 through December 2022 was collected and analyzed. Reports for crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib,and lorlatinib were filtered. We used the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA version 25.1). Disproportionality analyses were conducted to detect AEs signals for every ALK inhibitor by calculating reporting odds ratios (RORs). Reports were considered statistically significant if the lower limit of the 95% CI did not contain value 1.
Results: During the 2012-2022 observation period, 4508 reports of suspected adverse reactions to all ALK inhibitors were reported to EudraVigilance, with crizotinib being the most frequently reported (43.4%), followed by alectinib (28.0%), lorlatinib (13.6%), ceritinib (9.0%) and lastly brigatinib (6.0%). The most common adverse event reported in EudraVigilance for each drug include oedema for crizotinib, diarrhoea and nausea for certinib, fatigue for alectinib, elevated blood creatine phosphokinase levels for brigatinib and hypercholesterolaemia for lorlatinib. Disproportionality analyses of selected adverse events revealed significant differences between ALK inhibitors. Oedema was significantly related to crizotinib (ROR 1.57) and lorlatinib (ROR 1.60), hepatotoxicity to crizotinib (ROR 1.86), nausea and vomiting as well as diarrhea to crizotinib (ROR 1.95 and 1.55) and ceritinb (ROR 3.64 and 3.39), constipation to alectinib (ROR 3.16), eye disorders to crizotinib (3.02), photosensitivity to brigatinib (ROR 8.77) and alectinib (2.49), hypertension to brigatinib (17.76) and pnemunotis to alectinib (ROR 1.53) Lorlatinib was also signifcantly related to hyperlipidemia and psychiatric disorders (exact ROR to be evaluated).
Conclusions: This study highlights significant variability in the safety profiles of ALK inhibitors, with each drug associated with distinct adverse events as reported in the EudraVigilance system over a decade. It also indicates the importance of tailored patient management strategies based on the specific ALK inhibitor used.
